end tidal co2 range cpr
What does low ETCO2 mean. PaCO2 PetCO2 End tidal measurement from expired or exhaled air PaCO2 Arterial blood gas sample End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S.

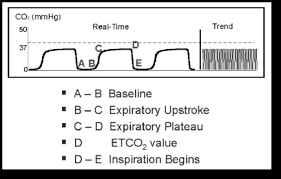
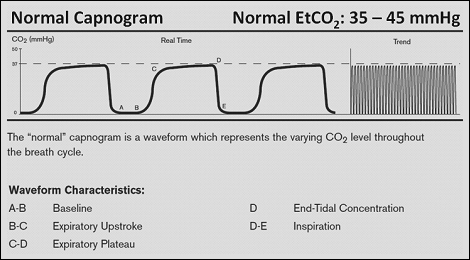
. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression generating reasonable pulmonary blood flow justifying continuation of resuscitation. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC.
The current guidance recommends an end-to-end carbon dioxide ETCO2 concentration of 4. Non-grid Solar Thermal Technologies Solar Tunnel Dryer A Promising Option for Solar Drying Biomass as a Source of Energy. Current guidance recommends an end- tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 of 4045 kPa 300 338 mm Hg to achieve a low- normal arterial partial pressure of CO2 PaCO2 and reduce secondary brain injury.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. The power consumption is 5 kPa 30. A prospective observational study.
What Is End Tidal Co2 Range. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 correlates with systemic blood flow and resuscitation rate during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and may potentially direct chest compression performance. When a capnometer is available and the machine is warmed-up connection to the ventilatory circuit takes CPR whether ventilating via bag-mask laryngeal.
End tidal co2 range cpr Tuesday March 15 2022 Edit. Remember the cells are going to use this oxygen create the CO2 but I still have to have adequate cardiac output a working pump to pump that CO2 all the way back to the lungs so it can be exhaled and measured. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg.
Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2. What should end tidal CO2 be kPa. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs.
Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2 therefore monitoring of ETCO2 provides very useful information to guide treatment during CPR 8 - 10. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR adequate chest compressions generate a cardiac output of 17 to 27 allowing CO 2 circulation for exhalation.
Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement in and out of the lungs ventilation CO2 production from cellular metabolism and. Between 3540 mmHg A normal EtCO2 is considered between 3540 mmHg however results may be influenced by various physiological factors. What is the normal range of end tidal CO2.
This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR ETCO2 concentration is a reliable index of effective heart compression during CPR which is associated with cardiac output 7 8. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector.
We compared ETCO2-directed chest compressions with chest compressions optimized to pediatric basic life support guidelines in an infant swine model to. What is normal PETCO2. 2 USES DURING CPR 7 CONFIRM ADEQUACY OF CHEST COMPRESSIONS.
This is exactly what were using end-tidal CO2 for in ACLS. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. Although certain ETCO2 cut-off values appears to be a strong predictor of mortality the utility of ETCO2 cut-off values during CPR to accurately predict the outcome of resuscitation is.
Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. In the field monitoring ETco 2 during endotracheal-tube placement can verify correct tube placement and indicate tube dislodgement during transport.
Usually in the field Im using end-tidal to tweak my ventilator. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement in and out of the lungs ventilation CO2 production from cellular metabolism and.
Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
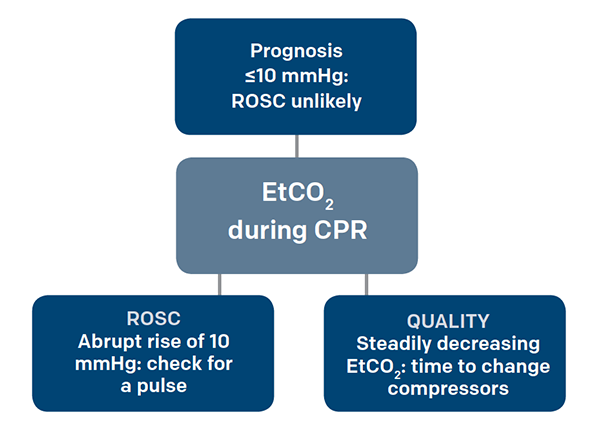
Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC. ETCO2 values during CPR do correlate with the likelihood of ROSC and survival and therefore have prognostic value. Properly administered capnography can help to identify lower end tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 levels so that appropriate changes in CPR such as rate or force of compression can take place.
In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. The absence of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow often results in CO 2 levels that fall abruptly. What Should End-tidal Co2 Be Kpa.
End Tidal CO2 Monitoring and Capnography. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is readily available easily used and a standard of care in the operating suite and in the critical care setting. This is an example of capnography during CPR.
Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value. By lowering the arterial partial pressure of CO2 PaCO2 to 8 mm Hg secondary brain injury can be reduced.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC.

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Basics Of Waveform Capnography Waveform Capnography Grepmed

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice